These networks tend to be responsible for the entire range of unbranded goods that would be sold in informal markets
India is distinctive because the last-mile of delivery is enabled by unorganised, entrenched small-scale traders
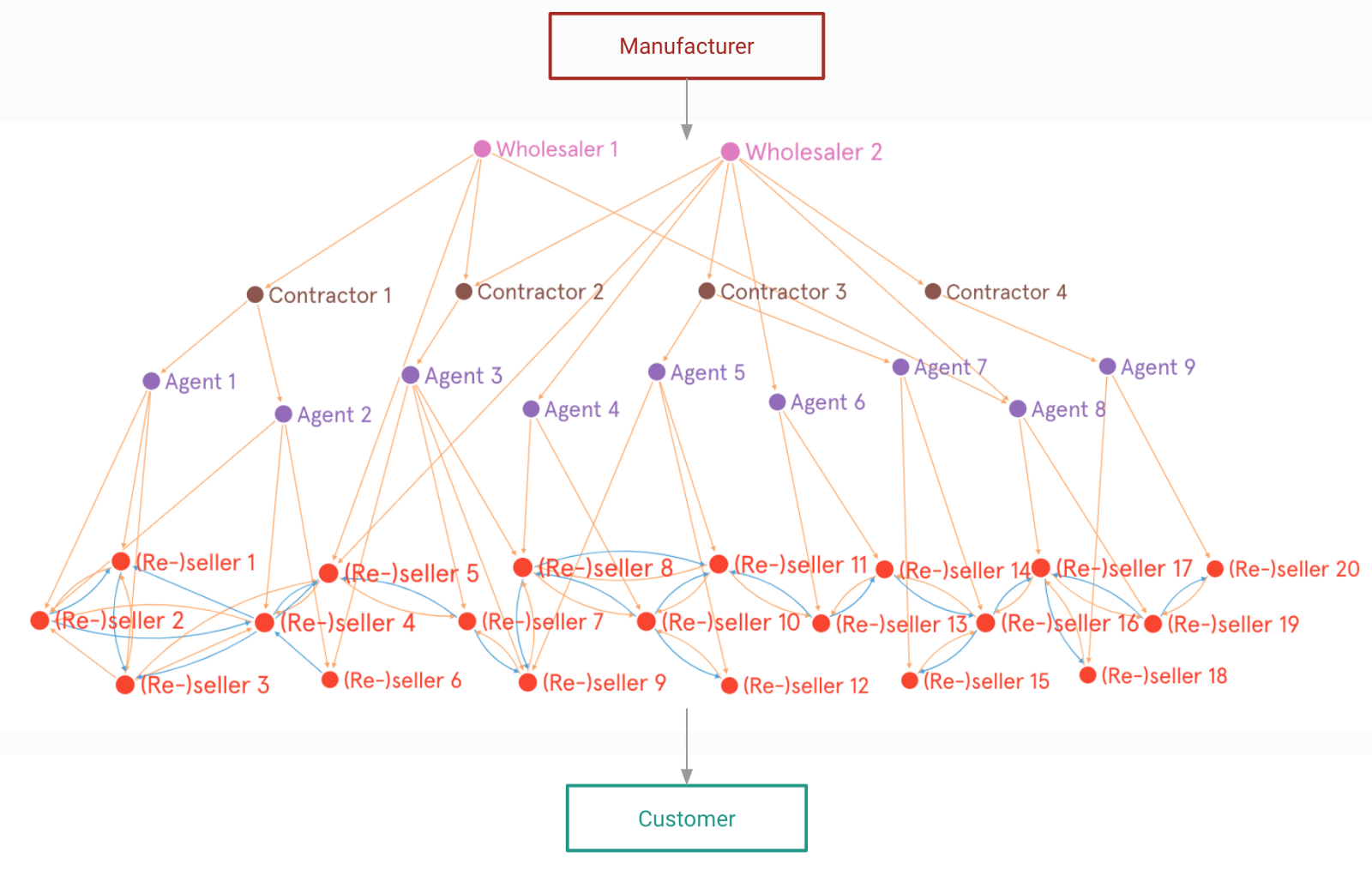
This “blackbox” is dominated by traders — wholesalers, contractors, agents and retailers — taking on multiple roles.
Contrary to the global trend where technology is “disrupting” industries, we believe technology must enable the bottom-up transformation of existing business structures in India: we refer to these unorganised networks as “blackbox delivery networks”.
The Power Of Blackbox Delivery Networks
Through our investments in companies leveraging such networks (most centrally — Meesho), we have closely observed the latent opportunity of inserting technology into these complex networks.
These networks tend to be responsible for the entire range of unbranded (non-standard) goods that would be sold in informal markets, such as electronics, fashion products, household supplies, fruits & vegetables, even travel experiences, financial products and more.
By adding technology to similar networks across industries, we believe existing business structures can be leveraged to quickly scale new ventures — particularly addressing goods and services for the mass-market, tier-2 India, consumer.
Existing Business Structures
On the surface, India’s appearingly disorganised and unstructured ways of getting things done hide the complexity and incredible efficiency behind the curtain.
For instance, the dubbawala network in Bombay delivering 200,000 home-cooked lunches every day is one such example of a blackbox delivery network.
Globally: The Conventional Supply Chain Model
Typically, supply chains have been organised in a linear model as below:
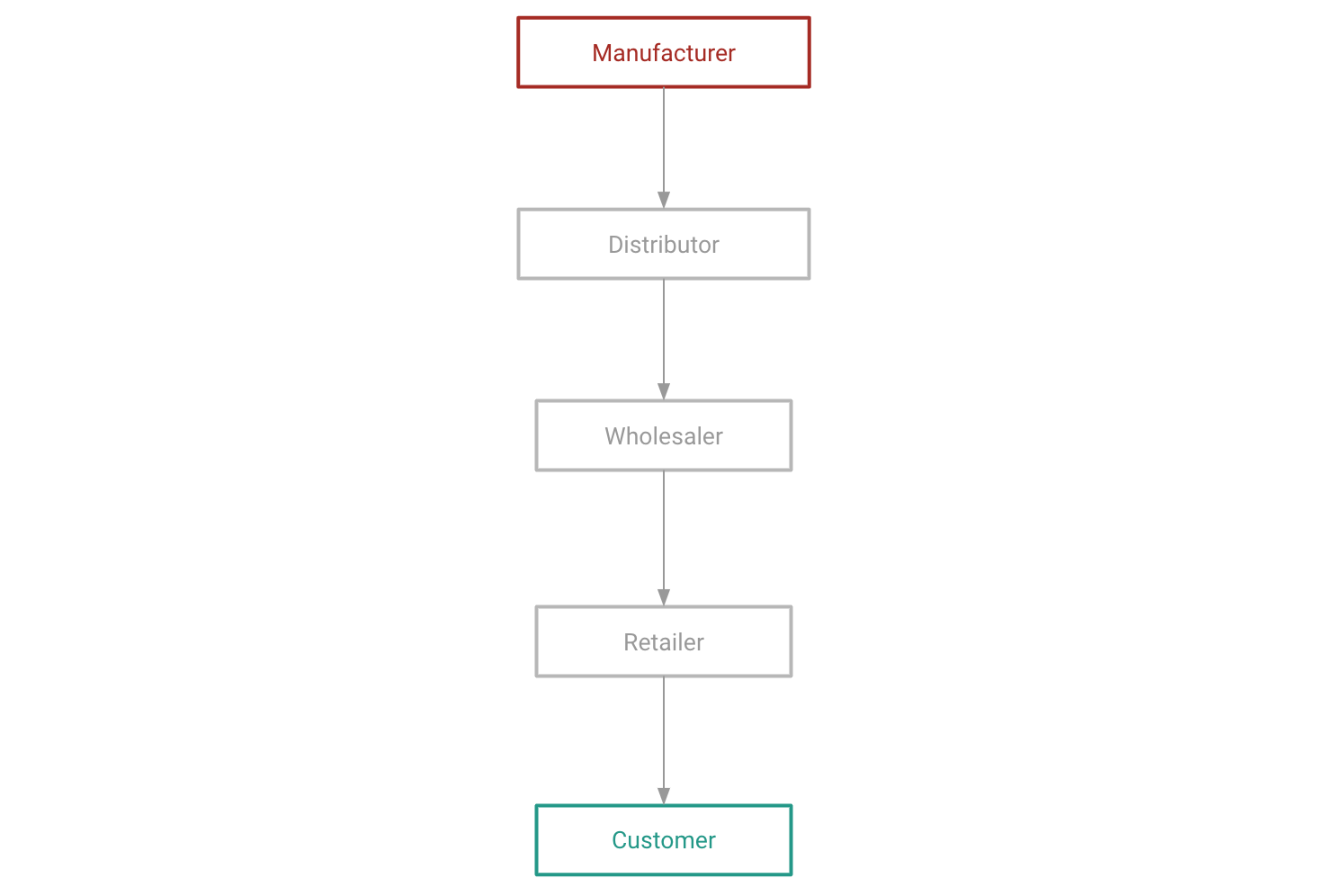
While there are typically layers of intermediaries and two-way interaction between players, interaction is primarily between parties in fixed roles in different vertical levels of the supply chain.
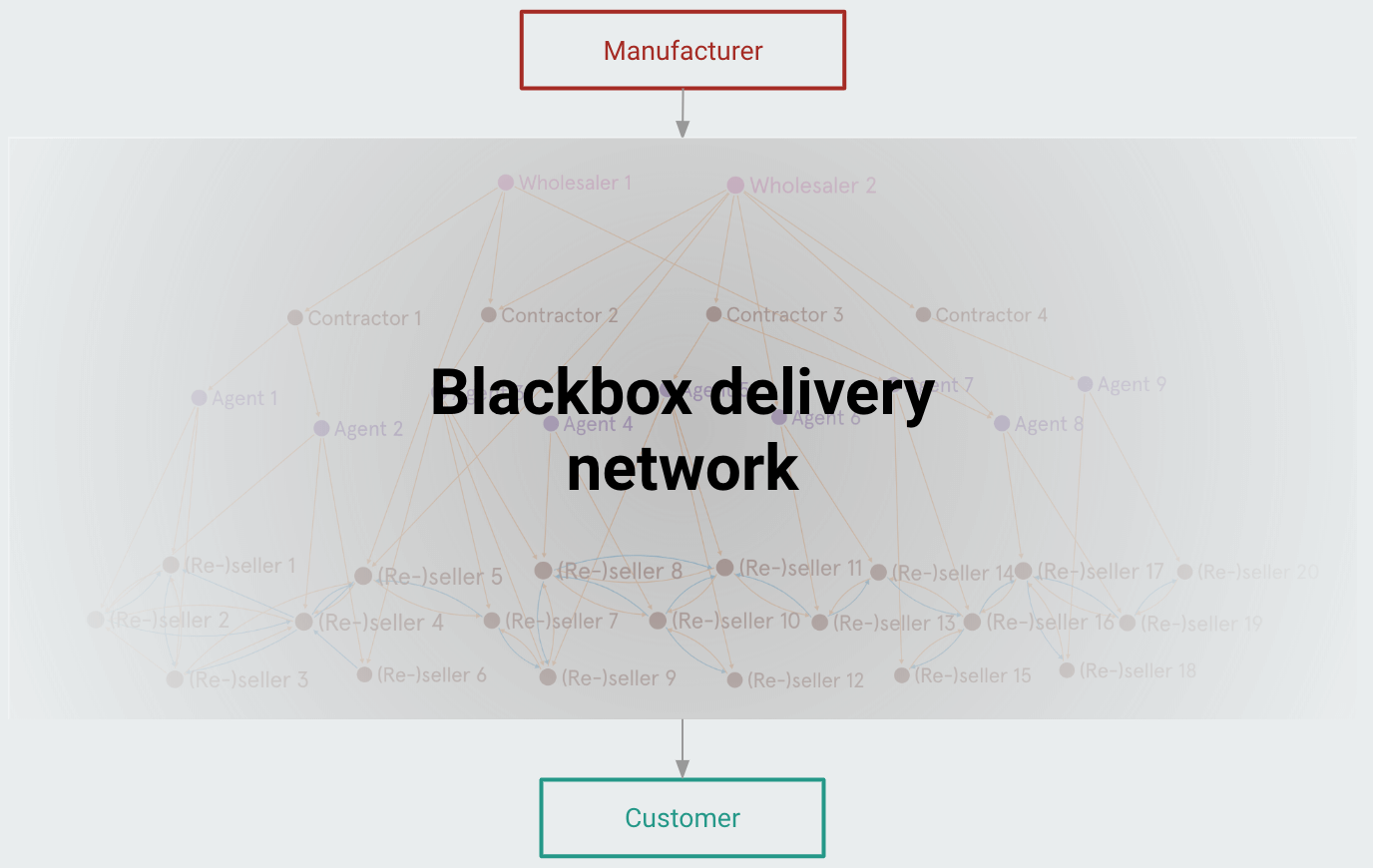
In India: The Blackbox Delivery Network
Globally, centrally-planned delivery networks ensure a smooth last-mile experience to consumers. But India is distinctive because the last-mile of delivery is enabled by unorganised, entrenched small-scale traders operating in blackbox delivery networks.
These “disorganised” supply chains in Indian industries start to splinter as we get closer to the consumer.
“After visiting India and seeing that it still functions amidst all the chaos… I finally believe there must be a god!”
– John Galvin
This “blackbox” is dominated by traders — wholesalers, contractors, agents and retailers — taking on multiple roles.
Their distinguishing characteristic is that they don’t simply interact vertically along the supply chain, but also across the same level of the supply chain; e.g. retailers sell products to one-another; they are thus also “re-sellers”.
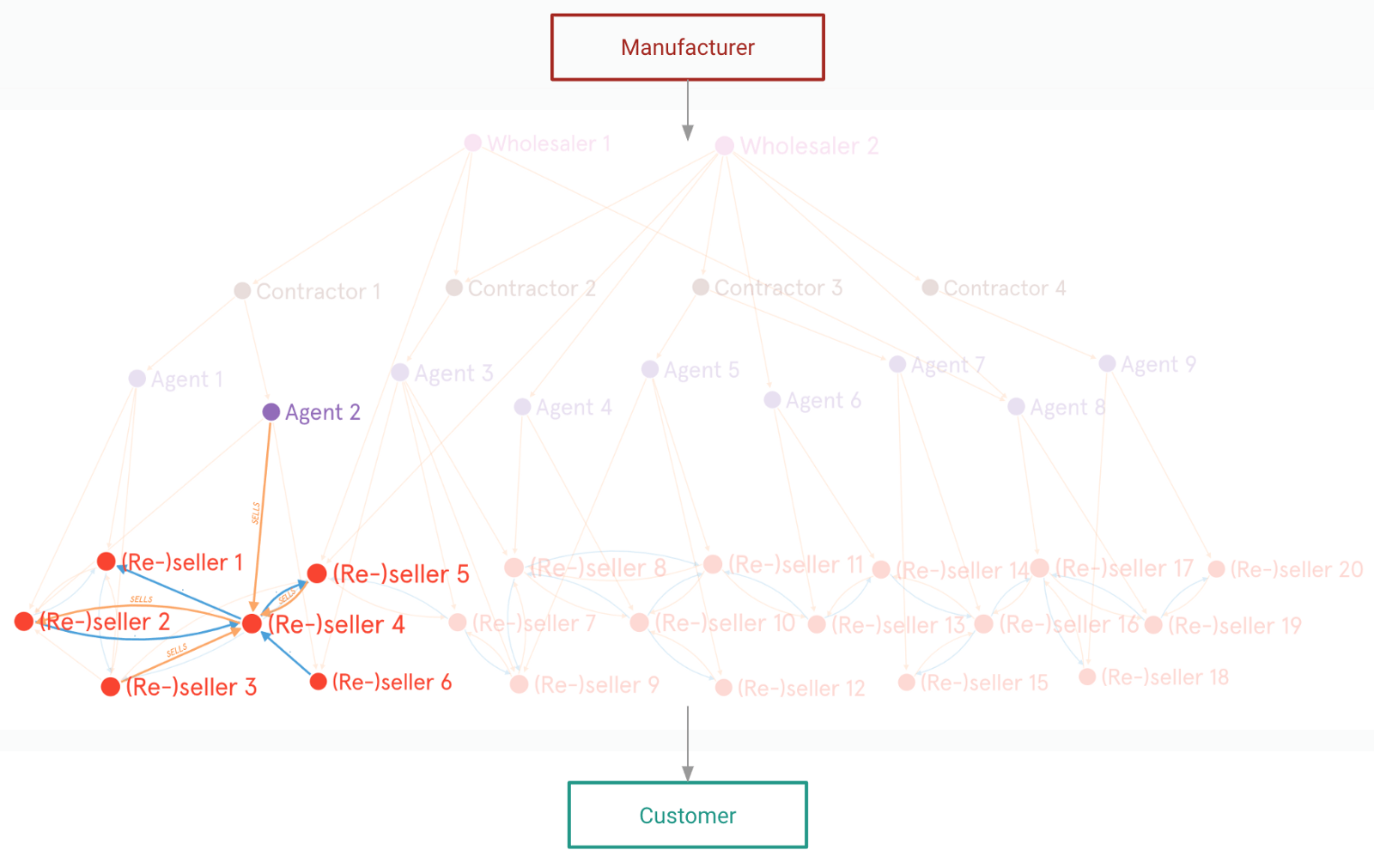
These traders form individual nodes in a massive, densely-connected, living network. They are the micro-entrepreneurs behind the blackbox: typically individuals or family units operating together.
A Blackbox Delivery Network In Action
Using the fashion industry as an example, we identify the different roles in such a blackbox network.
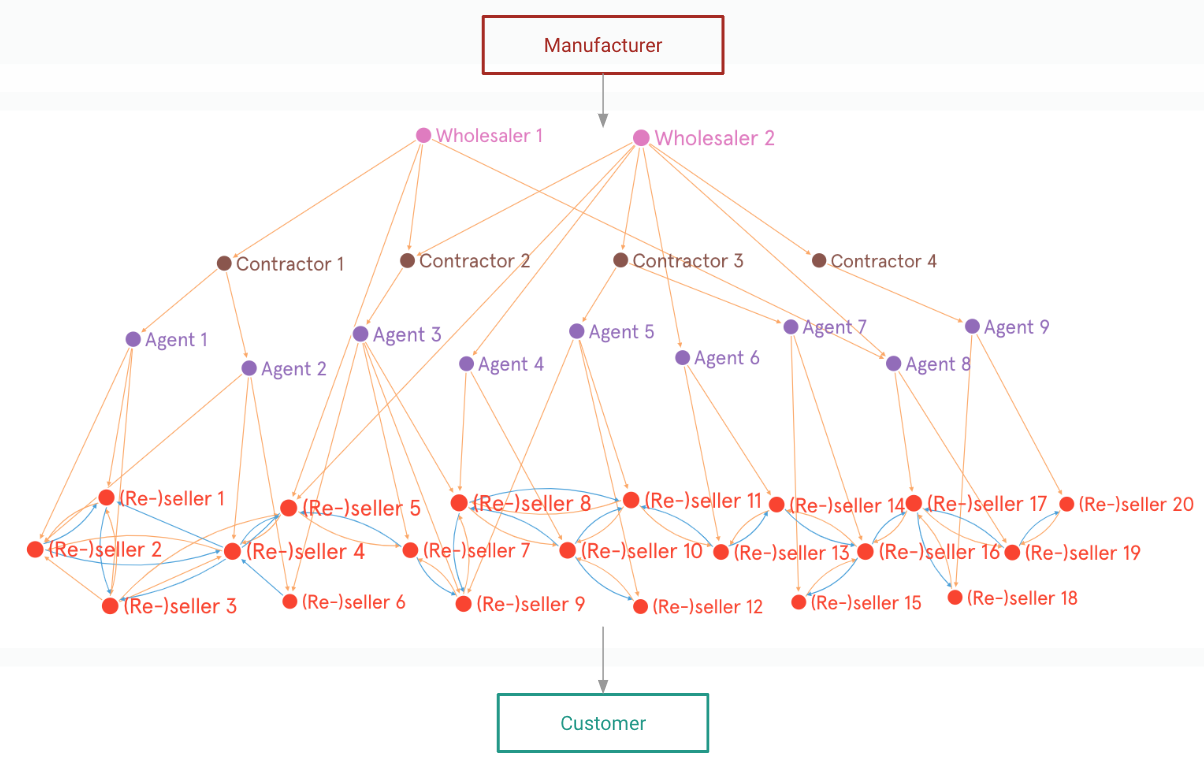
→ Wholesalers source products from manufacturers, often through distributors.
→ Each product category has regional wholesaler hubs.
For instance, the national hub for fashion products is in the city of Surat. Other regional wholesalers aggregate local supply, e.g. winter-wear in Ludhiana, sports goods in Jalandhar, etc.
→ The conduit between wholesalers and retailers is typically an agent.
Individuals need little market knowledge to become agents — they may take an agent job part-time, or as a stop-gap, or even become agents for many different product categories from different wholesalers.
→ Over time, the more enterprising agents grow their business by becoming contractors (thekedars) — they recruit other agents and manage them.
Retailers have a very strong pulse of demand because they engage closely with customers (“Sir finest material, and I give you best price”). As they observe trends and hear customer feedback, they tell an agent to source appropriate inventory for them.
Visit Khan Market in Delhi the next time you would like to buy fabrics for a custom shirt, and you will observe this in real-time!
→ Customers make frequent visits to retailers at local stores or markets to browse for products they may like. They visit frequently because products are made in small batches and there’s always new supply.
If the customer is looking for a specific style, they ask the retailer.
→ Sometimes the retailer knows that another retailer at a nearby store might have what the customer wants so he sends a runner (“chhotu”) over to go fetch samples.
The inventory is placed in front of the customer and — if the customer buys the product — the seller inculcates a mark-up from the other seller he sourced from.
 → This complementary relationship between such retailers sees them each take on the role of a (re-)seller: selling products to each other when convenient.
→ This complementary relationship between such retailers sees them each take on the role of a (re-)seller: selling products to each other when convenient.
(Re-)sellers have a high-touch relationship with one another and operate on the basis of trust. Thus, informal credit and routine settlements are a feature that enables rapid inventory turnover, and low cash flow requirements & costs.
At almost every level, the relationships that enable a business to happen are individual in nature.
Business occurs not between individuals, but between closely-connected individuals. It is this trust and a rich, interwoven network of interactions that elevates them as a whole into a collective equilibrium of profitable business.
Next
The above covers the way business works before technology enters the equation. In a future note, I’ll highlight a playbook for companies thinking about inserting technology into these blackbox delivery networks.

























 Ad-lite browsing experience
Ad-lite browsing experience